Fetal bovine serum (FBS) is an indispensable cell culture media supplement used for in vitro cell culture workflows in research and industrial laboratories. Culture media containing serum creates an artificial environment for growing tissue-derived cells that recapitulate physiological conditions. Cell culture media provides a source of energy and nutrients essential for cell growth and function. Serum provides cells with growth factors, amino acids, sugars, and hormones needed for cell proliferation, cell maintenance, cell adhesion to the cell culture support and support for signaling processes. The addition of serum can help maintain the pH of the media and protect against mechanical damage experienced when manipulating cells.

How is FBS obtained?
FBS is collected from the blood of fetuses from pregnant cows deemed fit for consumption. Blood is collected aseptically, refrigerated, and allowed to coagulate. Upon centrifugation, the serum is separated from the clotted blood cells. Blood collection is only undertaken at licenced facilities and includes animals with approved health statuses. The appropriate competent authority inspects FBS facilities to control quality standards. Working alongside governments, the Office International des Epizooties - OIE (World Organization for Animal Health) work to control the spread of infectious animal diseases.
Some companies still have issues with the traceability of their products — information on the origin of animals and animal health records. Ensuring traceability is important and can circumvent inconsistency between lots of sera and variations in the characteristics of the products. The industry body, the International Serum Industry Association (ISIA), was formed to promote traceability and compliance in the practices associated with animal-derived products. Companies affiliated with ISIA have their facilities independently audited and comply with international traceability standards, including collecting and examining documents related to processing, transportation or commercial activities. LubioScience work with companies specializing in producing FBS, Atlas Biologicals and Biowest. Both companies, established in the late 1980s, are committed to ensuring complete traceability of their sera products and are ISIA traceability certified.
Different types of FBS
Serum can be taken from animals of different ages. Whilst FBS is taken from fetuses, newborn calf serum (NBCS) is acquired from newborn calves less than 20 days of age. Adult bovine serum is taken from cattle older than 12 months. The serum type affects the biochemical composition. The choice of serum depends on the cellular application and cell type.
One of the most prominent differences between FBS and newborn calf serum is the level of circulating antibodies. NBCS has higher levels of immunoglobulins (IgGs) than FBS, as the first feed or colostrum from the mother to the calf is rich in antibodies(1). Another way to differentiate between serum sources is gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels. GGT is a transferase present in serum and on the surface of different cell types and is particularly active in the liver(2). The enzyme is responsible for the metabolism of the antioxidant glutathione. Like, IgG, GGT is found in colostrum, circulating in the blood. This results in higher serum GGT in NBCS compared to FBS(1). A veterinary screen can be used to detect IgG and GGT.
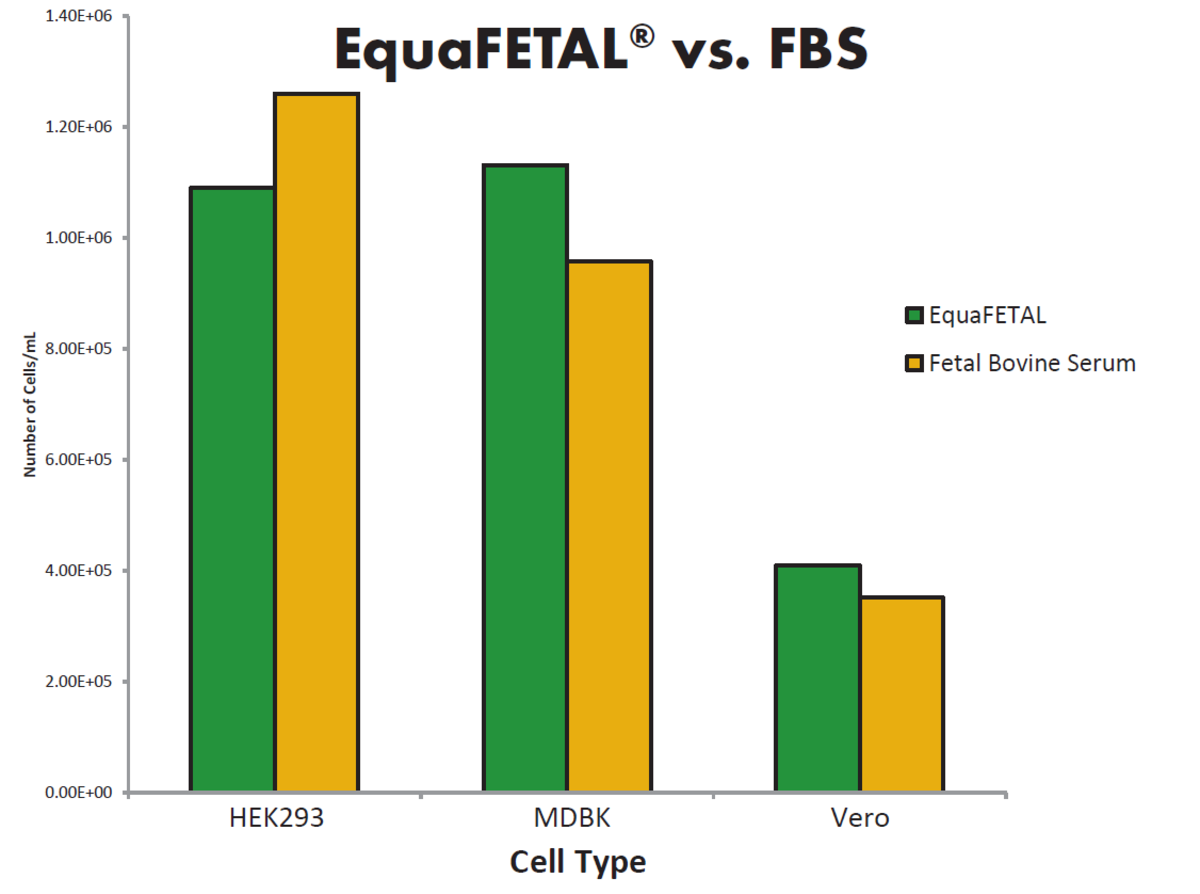
To combat differences in FBS composition in different categories of serum, Atlas Biologicals have developed a FBS alternative serum, EquaFETAL. EquaFETAL is derived from bovine animals after birth. Unlike NBCS, EquaFETAL has comparable levels of IgG and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) as FBS. Additionally, Atlas Biologicals consistently report the biochemical composition of EquaFETAL on the certificate of analysis of each product. EquaFETAL performs effectively in cell culture applications and can be employed with the same cell lines as FBS.
Different preparations of FBS
As FBS is a complex mixture of biomolecules, additional preparatory steps may be needed for certain applications. FBS contains complement proteins. For particular cell types, antibodies present in the serum can bind to the cells, activating complement proteins and resulting in the lysis of cells.
- Heat-inactivated FBS — heating the serum to 56°C for 30 minutes — inactivates complement proteins.
- Another preparation of FBS involves IgG depletion. IgG in serum may hamper the purification of monoclonal antibodies from hybridoma culture. IgG can be removed from serum by exploiting the ability of IgG to bind to Protein A with a high affinity. Sepharose columns covalently coupled with Protein A can be used to process FBS and reduce or deplete IgG levels.
- Another treatment of FBS is charcoal stripping. This treatment uses activated carbon resin to reduce the concentration of steroid hormones (estradiol, progesterone, cortisol), which are lipophilic (having good solubility in lipids and fats). For receptor studies, charcoal/dextran-stripped FBS proves helpful because of its reduced concentration of steroid hormones.
- A type of physical inactivation treatment of FBS involves gamma-irradiation. Although FBS is tested for contaminants according to regulatory requirements, very low levels may still be present, posing cell culture problems. Treating FBS with gamma-irradiation (electromagnetic radiation with shorter wavelengths) reduces pathogen contamination from viruses and mycoplasma. The treatment does not affect the quality of the serum and has no effect on hormones, osmolality, pH and electrophoretic profile. The use of gamma-irradiated FBS is particularly important for producing viruses and vaccines.
- Filtration can also be used to process FBS. Filtering the sera using a 0.45 µm filter can be used to remove flocculent material arising from the presence of fibrinogen, which could impede experiments. For culturing cells that are sensitive to endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide, LPS), such as macrophages and immune cells, a low endotoxin FBS may be needed. Trace amounts of endotoxin (LPS) are found in FBS. However, ultra-low endotoxin FBS undergoes additional filtration in sterile conditions to guarantee < 0.1 EU/ml endotoxin levels. Further, ultrafiltration can remove contaminants in extracellular vesicles (EVs) and protein and RNA aggregates, which are known forms of contamination from FBS. EV contamination can be problematic. EV-depleted FBS is beneficial in clinical workflows requiring standardization or for EV studies.
Serum from other sources
Serum from animals other than cows has also been shown to be useful for research applications. For example, horse serum is important in maintaining hematopoietic progenitor cells in culture and keeping them in a less differentiated state. Serum is also available from other animals, including goats, donkeys, rabbits, lambs and pigs.
LubioScience's range of serum
LubioScience are a trusted provider of critical life science reagents, such as animal sera. Please visit our website for more information or contact us for further details.
Supplier

Biowest
Biowest is the leading manufacturer of animal sera in Europe. We have a special offer for FBS and can store purchased bottles for free.

Atlas Biologicals
Their FBS is manufactured with raw materials that are 100% traceable to the source of the animals within the United States and selected U.S.D.A. approved countries.
References
- Cheever, M., Master, A., & Versteegen, R. (2017). A Method for Differentiating Fetal Bovine Serum from Newborn Calf Serum. Bioprocessing Journal: Trends and Developments in Bioprocess Technology, 16.
- Dominici, S., Paolicchi, A., Corti, A., Maellaro, E., & Pompella, A. (2005). Prooxidant reactions promoted by soluble and cell-bound γ-glutamyltransferase activity. In Methods in Enzymology (Vol. 401).
- Figure 1. https://www.atlasbio.com/what-is-an-fbs-alternative/