RNA isolation can be a demanding procedure in molecular biology. Researchers often face RNA degradation, low yield or purity, and unwanted DNA contamination. Different biological materials present their own challenges. For example, microbes such as gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria, fungi, and archaea may have robust cell walls that are difficult to break. Samples like faeces or plants can contain inhibitory compounds such as polyphenolics, humic or fulvic acids, and tannins that may co-precipitate with RNA and compromise downstream applications including RT-qPCR.
In this guide, experienced researchers share practical advice for improving RNA isolation results and recovering high-quality, DNA-free RNA.
Preserving RNA immediately after collection
RNA molecules are inherently unstable and degrade quickly when exposed to RNases. Many sample types naturally contain high levels of these enzymes. The most effective way to preserve RNA integrity is to stabilise the material as soon as it is collected.
Common preservation approaches include snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, immersion in a dry-ice ethanol bath, or storage at –80 °C. While effective, these methods can cause freeze–thaw damage to nucleic acids and may not be practical during fieldwork or at remote collection sites.
Recommended RNA preservation strategies:
Dissolving the sample directly into a lysis buffer that inactivates RNases, such as TRIzol® or RNA Lysis Buffer. The material can then be processed immediately or stored at low temperature.
Placing the sample in a stabilisation reagent such as DNA/RNA Shield, which protects RNA at room temperature for extended periods. This is particularly useful when handling valuable clinical material such as biopsies or whole blood, or when working outside a laboratory environment.
Achieving complete sample lysis
Efficient cell disruption is essential for high RNA yield and quality. However, not all cell types respond equally to the same method. Blood-derived cells such as lymphocytes or PBMCs and microbial cells often require more than a detergent-based buffer.
Better results can be achieved by combining chemical lysis with mechanical disruption such as bead beating, or by including an enzymatic treatment such as proteinase K or lysozyme before extraction.

Figure 1: Total RNA extracted from E. coli cells using lysis buffer combined with bead beating (samples 1–3) compared with buffer alone (samples 4–6). Mechanical homogenisation produces clearer ribosomal bands and higher RIN values. Agilent 2200 TapeStation®.
Complete lysis also supports smoother processing in column-based RNA isolation methods. Without it, column clogging, buffer carryover, incomplete DNA removal, and poor elution can occur. Zymo Research has tested and optimised lysis protocols suitable for a wide variety of sample sources.
Eliminating DNA contamination
A frequent challenge in RNA isolation is residual DNA. This contamination can affect absorbance-based quantification such as Nanodrop readings, giving artificially high RNA concentrations. It can also interfere with sensitive downstream analyses such as RNA sequencing.
DNA can be removed through TRIzol® phase separation, by using DNA removal columns, or by applying DNase treatment during the extraction process.
Visual inspection of RNA on an agarose gel or with an Agilent TapeStation® can quickly reveal high-molecular-weight DNA above the 28S ribosomal RNA band (Figure 2). For applications with high sensitivity to DNA, qPCR or Qubit assays are recommended.
Many Zymo RNA isolation kits integrate on-column DNase I treatment, which saves time by eliminating the need for separate clean-up steps after extraction. This approach helps ensure that the RNA is ready for immediate use in downstream applications.
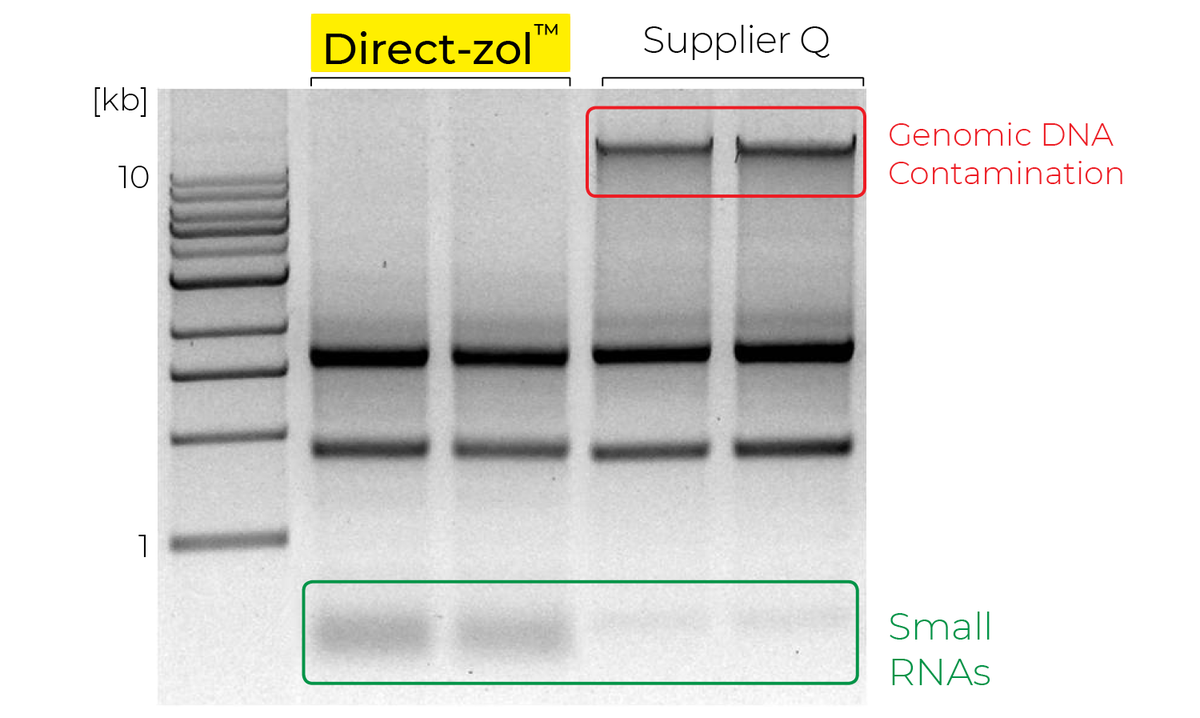
Figure 2: Agarose gel showing RNA profiles from human epithelial cells. The sample prepared using a Zymo RNA isolation kit is free of genomic DNA and includes more small RNA than those prepared with Supplier Q or Supplier P kits.


Figure 3: RT-PCR analysis of RNA isolated from 10⁶ human epithelial cells. The Zymo Quick-RNA kit (green) shows no detectable DNA amplification compared to Supplier Q.
Selecting the right RNA isolation kit
No single method works for all types of RNA extraction. The choice of kit depends on the sample material, input amount, and desired throughput. Zymo Research provides a range of kits adapted to different needs, from small-scale micropreps to high-throughput magnetic bead formats.
The table below lists recommended products for various sample types, which may help when comparing types of RNA extraction methods.
| Sample type | Recommended kit |
|---|---|
| Samples in TRIzol® | Direct-zol RNA Kits |
| Cells, tissue, blood, other fluids | Quick-RNA Kits |
| Viral RNA | Quick-RNA Viral Kit |
| Whole blood | Quick-RNA Whole Blood |
| Urine | ZR Urine RNA Isolation Kit |
| Tissue sections | Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System |
| FFPE samples | Quick-RNA FFPE Miniprep |
| cfRNA from serum, plasma, CSF, amniotic fluid | Quick-cfRNA Serum & Plasma Kit |
| Faeces, soil, biofilm, water, culture | ZymoBIOMICS RNA Miniprep Kit |
| Plant samples | Quick-RNA Plant |
| Microbial cultures | Quick-RNA Fungal/Bacterial Kits |
| Insects (mosquitos, bees, drosophila, ticks) | Quick-RNA Tissue/Insect Kit |
| RNA from enzymatic reactions, aqueous phase | RNA Clean & Concentrator Kits (RCC) |
| RNA from agarose gels | Zymoclean Gel RNA Recovery Kit |
| RNA with PCR inhibitors | OneStep PCR Inhibitor Removal Kit |
| Sample collection and RNA preservation | DNA/RNA Shield |
Key points for mastering RNA isolation
Recovering high-quality total RNA from any sample is possible when three principles are followed. First, preserve the material immediately after collection. Second, ensure complete and effective lysis. Third, remove any traces of DNA contamination.
By applying these steps, researchers can obtain RNA suitable for a wide range of downstream applications with reliable and reproducible results. Comprehensive kits that combine these features can simplify the workflow and are supported by technical specialists who can offer further guidance.
This article is based on an original post by Zymo Research. You can read the original here.
Featured supplier

Zymo Research
Zymo Research is a leader in molecular biology, offering a comprehensive range of products for DNA, RNA, and epigenetics research. Established in California in 1994, the company is renowned for its high-quality nucleic acid purification technologies, including kits and reagents for DNA and RNA clean-up, isolation, and sequencing. Zymo is also a pioneer in epigenetics, with products for DNA methylation analysis, chromatin analysis, and NGS library preparation. Each product is designed to be simple to use, reliable, and available at competitive prices, making them ideal for both academic and biopharmaceutical research.
