HMGB1 is a multifunctional protein with various roles in different cellular compartments. It is associated with various pathogenesis such as cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and multiple inflammatory diseases. HMGB1 has attracted the attention of both basic and clinical researchers as HMGB1 is a therapeutic target for a wide range of diseases. arigo offers a total solution to facilitate the HMGB1-related research.
The functions of HMGB1
Nuclear and cytosolic HMGB1
In the nucleus, HMGB1 acts as a DNA-binding protein for gene transcription, gene regulation and DNA repair. In the cytosol, HMGB1 induces autophagy by interacting with Beclin-1 which results in its dissociation from Bcl2 and the subsequent induction of autophagy.
Extracellular HMGB1
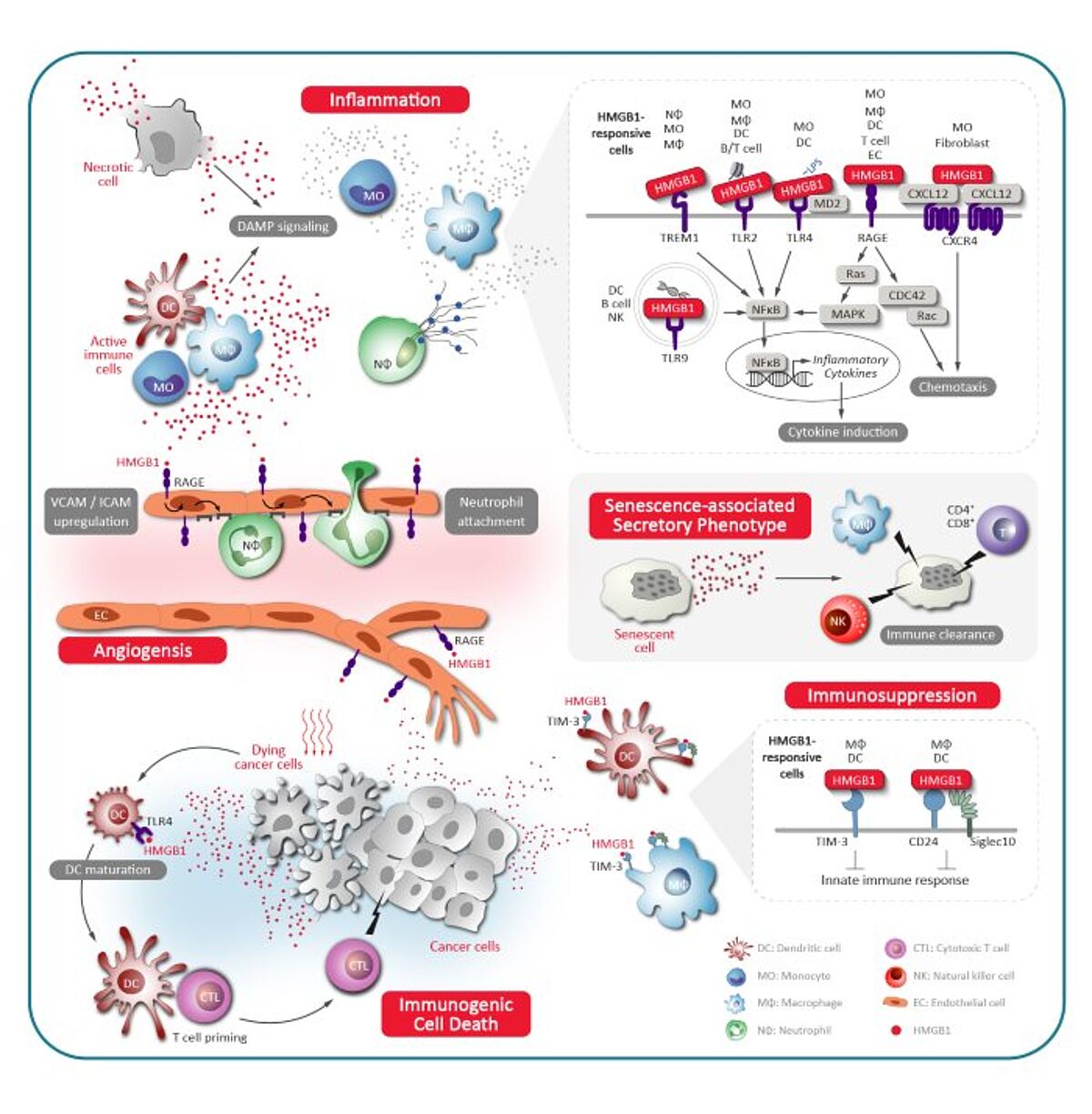
In the extracellular compartment, HMGB1 is passively released by necrotic cells and acts as a chemokine and DAMP (Damage-associated molecular pattern) to trigger inflammatory responses. Besides, HMGB1 is also secreted from activated dendritic cells and macrophages and functions as a cytokine, it acts as a ligand for RAGE, TLR-2 and TLR-4 thus activating the signal pathways and the following inflammation responses.
HMGB1 in inflammation
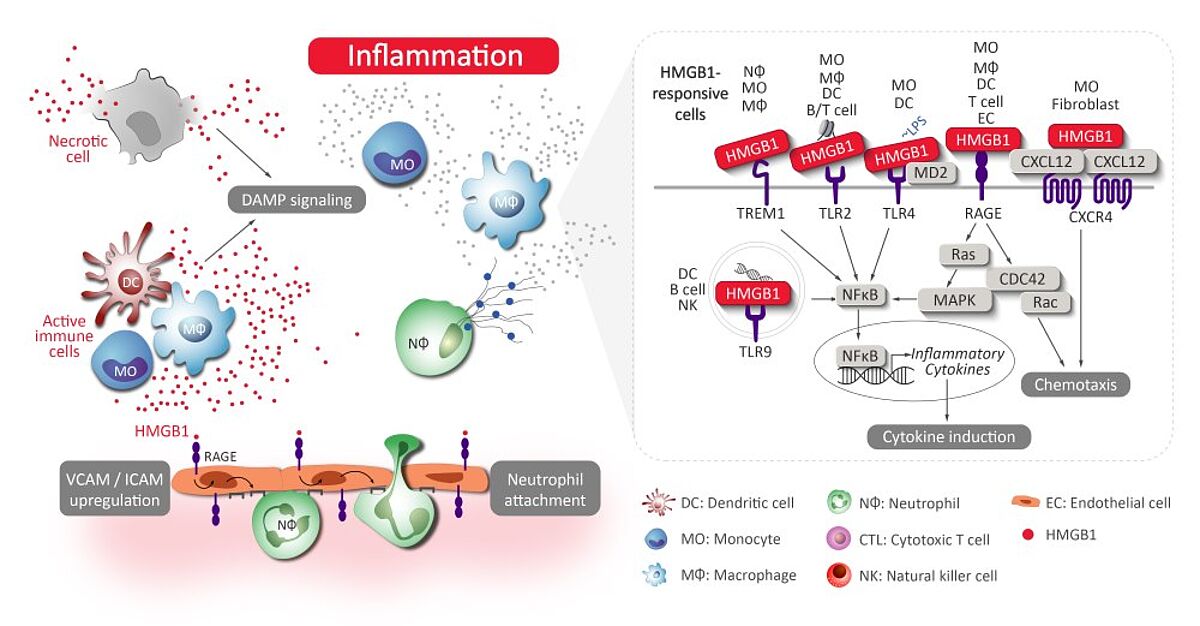
HMGB1 is a multifunctional protein that plays a central role in inflammation. When released extracellularly – either passively from necrotic cells or actively from immune cells like monocytes and dendritic cells – HMGB1 acts as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) and pro-inflammatory cytokine.
- HMGB1 promotes neutrophil recruitment – HMGB1 activates vascular endothelial cells to express cell adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1). Neutrophils undergo capture and rolling through interaction with these cell adhesion molecules, transmigrate across the vessel, and are recruited to the site of inflammation.
- HMGB1 induces NETosis – In addition to promote neutrophil recruitment, HMGB1 also induces NETosis. NETosis is a type of cell death that is characterized by the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which are composed of chromatin and granule proteins. NETosis allows neutrophils to kill pathogens. However, excessive NETs result to tissue damage and participate in pathogenesis of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders such as atherosclerosis, COPD, SLE, rheumatoid arthritis.
- HMGB1 induces production of inflammatory cytokines – In monocytes/macrophages, HMGB1 binding to TLR2/4 initiates the activation of NFkB signaling, resulting in pro-inflammatory cytokine production. (Red more about pro-inflammatory cytokines and NFkB signaling)
- HMGB1 triggers pyroptosis – Pyroptosis, an inflammatory cell death, promotes a rapid clearance of pathogens by enhancing the defensive responses. As a DAMP, HMGB1 initiates the formation of NLRP3 inflammasome which contributes to maturation of inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and IL-18 and formation of GSDMD pores, resulting release of inflammatory cytokines. (Red more about Inflammasome & Pyroptosis)
HMGB1 in the tumor microenvironment
HMGB1 has dual roles in tumor microenvironment (TME). During tumor development, HMGB1 acts as a pro-tumoral protein by promoting tumor growth, angiogenesis, immunosuppression, invasion and metastasis. However, HMGB1 also plays an anti-tumoral role by mediating immunogenic cell death (ICD) during chemoradiotherapy and enhance anti-tumor immunity. HMGB1 provides potentially therapeutic strategy for cancer chemoradiotherapy and immunotherapy.
- HMGB1 induces angiogenesis – Endothelial cells (ECs) play pivotal roles in tumor angiogenesis. Tumor-derived HMGB1 stimulates the migratory and sprouting capacity of ECs. Besides, HMGB1 also recruits and activate macrophages to produce angiogenic factors for vasculature formation.
- Immunosuppressive role of HMGB1 – In tumor microenvironment (TME), tumor-derived HMGB1 suppresses CD8+ T cell-dependent antitumor immunity by facilitating myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) differentiation and stimulating Treg-mediated immunosuppression. Moreover, HMGB1 binds to immunosuppressive receptor TIM‐3 on dendritic cells (DCs), interferes DC’s function and therefore inhibits the anti-tumor immune response.
- HMGB1 promotes invasion and metastasis – HMGB1 is highly expressed in a variety of malignant tumors. It promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), invasion and metastasis by HMGB1-RAGE signaling.
- HMGB1 activate immunogenic cell death (ICD) – ICD is a form of cell death resulting in an activation of immune response. ICD is triggered by damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) which include HMGB1 release. The dying cell-derived HMGB1 binds to TLR4 to induce DC maturation, antigen presentation and subsequent cytotoxicity mediated by CD8+ T cells. Monitoring HMGB1 release is common for evaluating the effects of chemoradiotherapy or ICD.
Arigo Biolaboratories offers the most comprehensive ELISA kits to facilitate HMGB1 research as well as the development of anticancer drugs. These ELISA kits provide three advantages compared to ELISA kits from other manufacturers.
Featured products
| Cat-No. | Item | Size | Price (CHF) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARG70220-100UG | Human HMGB1 recombinant protein (Active) (His-tagged, C-ter) | 100 ug | 904.00 |
| ARG66714-100UG | anti HMGB1 Neutralizing antibody [SQab20175] (low endotoxin) | 100 ug | 574.00 |
| ARG65863-100UG | anti HMGB1 antibody [SQab1711] | 100 ug | 560.00 |
| ARG81185-96WELLS | Human HMGB1 ELISA Kit | 96 wells | 831.00 |
| ARG81310-96WELLS | Mouse / Rat HMGB1 ELISA Kit | 96 wells | 831.00 |
| ARG81351-96WELLS | HMGB1 ELISA Kit | 96 wells | 831.00 |
In partnership with

Arigo Biolaboratories - Antibodies, antibody duos, ELISA
Arigo Biolaboratories are dedicated to developing the most comprehensive collection of antibody duos and antibody panels.
About Arigo Biolaboratories Shop for Arigo Biolaboratories products