What are bispecific antibodies?
A bispecific antibody drug (BsAb, BsMAb) is a synthetic protein capable of binding two distinct antigens, or two different epitopes on the same antigen, simultaneously. This dual specificity allows them to:
- Induce protein complex interactions.
- Interfere with receptor signalling.
- Inactivate signalling ligands.
- Activate immune cells.
BsAbs have been investigated for therapeutic applications in targeted drug delivery, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer immunotherapy.
By recognising two epitopes, bispecific antibodies can:
- Redirect T lymphocytes to tumour cells.
- Inhibit two signalling pathways at once.
- Target multiple disease agents simultaneously.
- Deliver therapeutic payloads directly to specific sites.
Structure and Function
Monoclonal antibodies provide the foundation for BsAb design. Early strategies involved reducing and reoxidising hinge-region cysteines in monoclonal antibodies to form bispecific molecules. Today, BsAbs fall into two main structural classes:
- IgG-based antibodies.
- Variable fragment (Fv)-based antibodies.
Depending on therapeutic application, BsAbs are grouped into three categories:
- Antibodies targeting two tumour antigens.
- Antibodies targeting one tumour antigen and one phagocytic molecule.
- Antibodies targeting two immune-related molecules.
The BiTE Mechanism
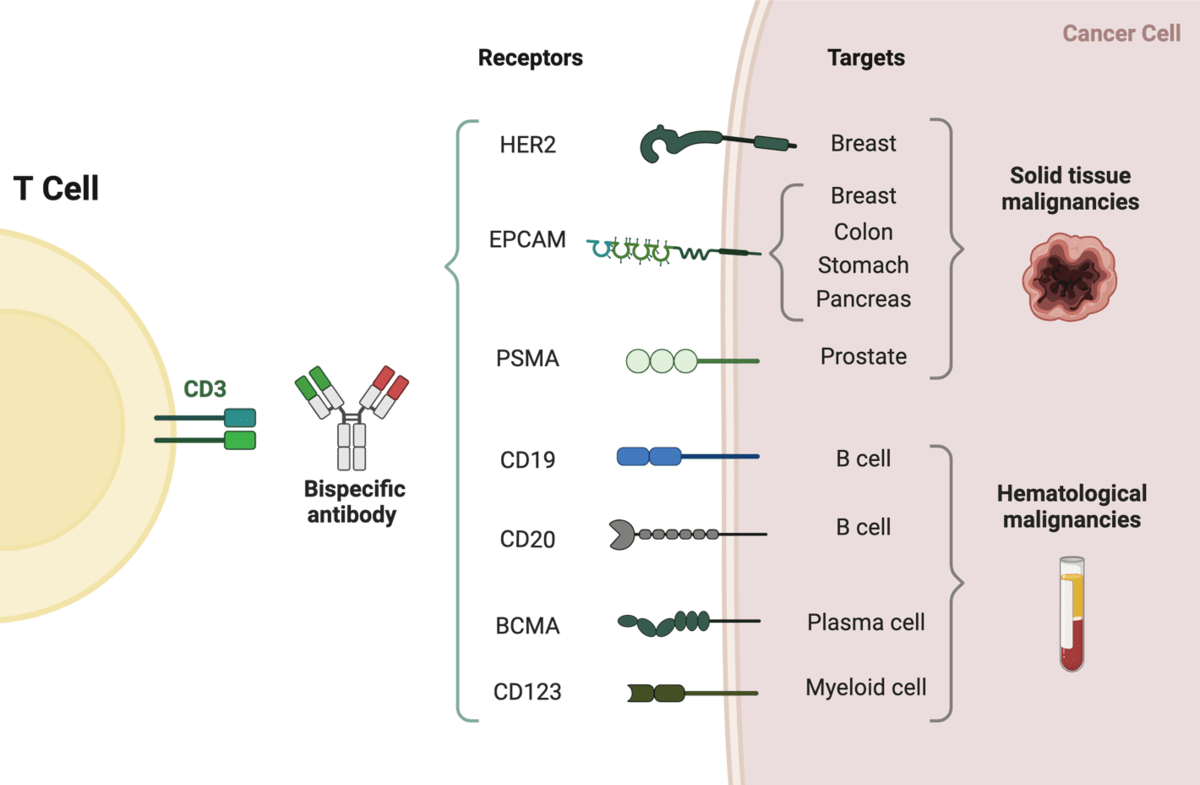
Bi-specific T cell engagers (BiTEs) are a subclass of BsAbs developed as anti-cancer agents. They harness the host immune system by directing cytotoxic T cell activity against tumour cells. A typical BiTE binds both a tumour-associated antigen and the CD3 complex on T cells, and therefore falls under the second category of BsAbs.
Each BiTE molecule contains two single-chain variable fragments (scFvs):
- Tumour-binding domain: targets antigens such as BCMA, CD19 or DLL3.
- T cell-binding domain: targets CD3 on T cells.
The scFv is composed of fused variable regions of heavy (VH) and light (VL) antibody chains, linked with a flexible peptide. Two scFvs joined by a linker create the dual-binding domains of a BiTE. Importantly, the tumour-targeting scFv can be adapted to different antigens, enabling off-the-shelf therapeutic flexibility.
Unlike natural antibodies, BiTEs directly connect T cells to tumour cells. This leads to T cell activation, proliferation, and enhanced tumour lysis, all without co-stimulation or MHC presentation²³.
Activated T cells then release cytotoxic proteins, including perforin and granzymes, which form pores in tumour cell membranes and trigger apoptosis.
Clinical Significance of BiTEs
Natural antibodies cannot directly recruit T cells, as T cells lack Fc receptors. By binding CD3, BiTEs bypass this limitation, enabling T cell activation and proliferation via antigen-specific signalling³⁴.
Key features of BiTE-driven T cell activation include:
- Requirement of tumour cell presence for T cell activation.
- Independence from co-stimulatory signals such as CD28 or IL-2.
- Reactivation of exhausted T cells exposed to tumour antigens.
The first BiTE therapy approved for clinical use was blinatumomab, which targets CD19 on both healthy and malignant B cells. It is effective at very low concentrations (10–100 pg/ml), inducing serial target-cell lysis in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma⁵⁶.
Compared to monoclonal antibody (mAb) drugs or combinations, BsAbs offer:
- Higher binding avidity.
- Greater cytotoxicity.
- Reduced drug resistance.
- Novel functionalities arising from their unique structure.
Clinical acceptance of BiTE antibody drugs
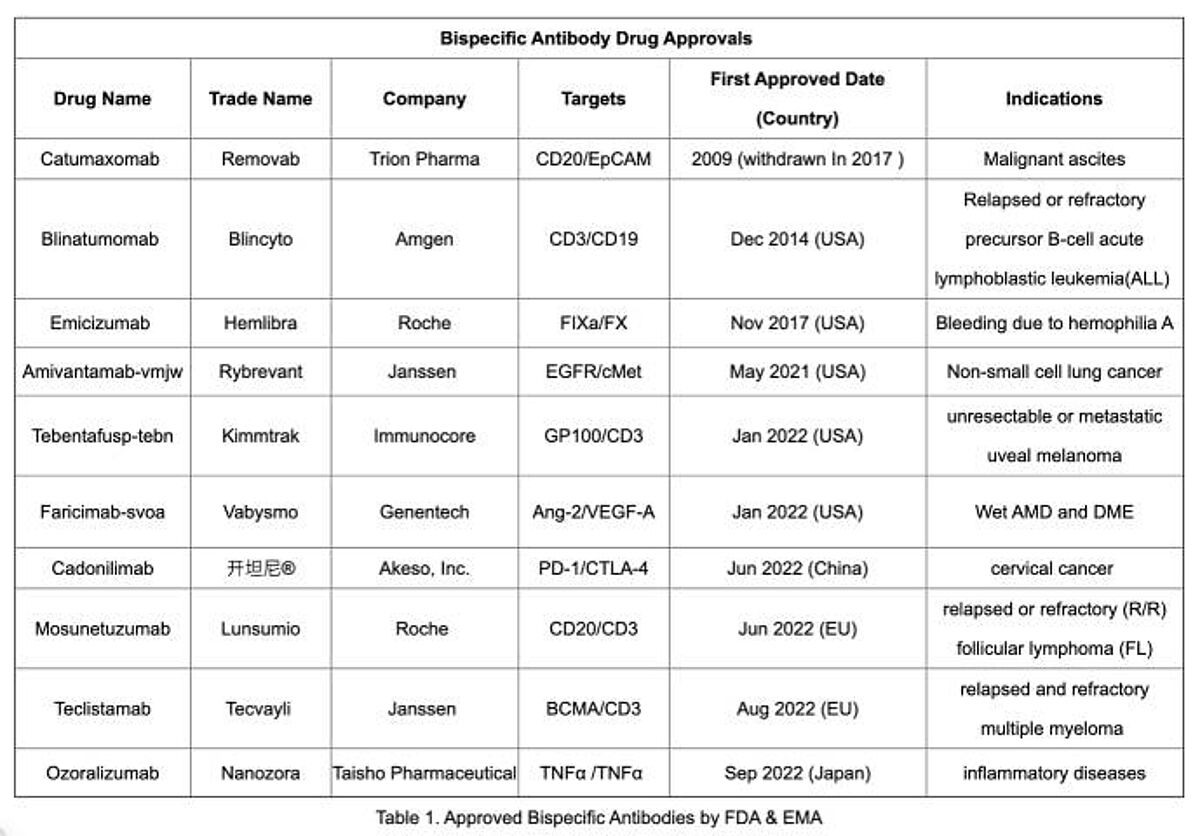
To date, nine bispecific antibodies have received global approval, including five FDA-approved agents:
- Blinatumomab
- Emicizumab
- Amivantamab
- Tebentafusp-tebn
- Faricimab-svoa
Bispecific antibody drug research
Developing and optimising BiTEs requires careful bioanalytical assessment. Accurate pharmacological quantification in vitro helps:
- Improve the therapeutic index of candidate drugs.
- Identify the most promising compounds early in discovery.
- Predict safe, pharmacologically active starting doses for clinical studies.
This is a key challenge in developing CD3-bispecific therapies.
Krishgen is the only commercial manufacturer currently offering ELISA kits specifically for bispecific antibody pharmacokinetic studies. With 40+ drug targets available in highly sensitive sandwich ELISA format, Krishgen supports BsAb research with robust analytical tools.
Example assays:
- Teclistamab: microwells pre-coated with recombinant BCMA protein; HRP-conjugated CD3 as detector.
- Blinatumomab: microwells pre-coated with CD19 protein; HRP-conjugated CD3 as detector.
References
Einsele, H. et al. The BiTE (bispecific T-cell engager) platform: development and future potential of a targeted immuno-oncology therapy across tumour types. Cancer126, 3192–3201 (2020). doi:10.1002/cncr.32909
Amgen. The shape of drugs to come: bispecific antibodies. Available at: https://www.amgen.com/stories/2018/08/the-shape-of-drugs-to-come/bispecific-antibody (accessed 2024).
Tian, Z., Liu, M., Zhang, Y. et al. Bispecific T cell engagers: an emerging therapy for management of haematologic malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol.14, 75 (2021). doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01084-4
Biochempeg. Approved bispecific antibody drugs. Available at: www.biochempeg.com/article/71.html (accessed 2024).
Brennan, M., Davison, P. F. & Paulus, H. Preparation of bispecific antibodies by chemical recombination of monoclonal immunoglobulin G1 fragments. Science229, 81–83 (1985).
Engelberts, P. J. et al. DuoBody-CD3xCD20 induces potent T-cell-mediated killing of malignant B cells in preclinical models and provides opportunities for subcutaneous dosing. EBioMedicine52, 102625 (2020).
Nagorsen, D. & Baeuerle, P. A. Immunomodulatory therapy of cancer with T cell-engaging BiTE antibody blinatumomab. Exp. Cell Res.317, 1255–1260 (2011).
Brischwein, K. et al. Strictly target cell-dependent activation of T cells by bispecific single-chain antibody constructs of the BiTE class. J. Immunother.30, 798–807 (2007).
Supplier

Krishgen Biosystems
Krishgen Biosystems is an original manufacturer of therapeutic antibody ELISA kits, HCP detection assays, immunotherapy assay kits, antibodies, proteins, assays for drug development.
About Krishgen Biosystems Shop for Kirshgen Biosystems products
