Recombinant antibodies
What are they?
Unlike monoclonal antibodies produced from a hybridoma (i.e. a fusion between an antibody-producing B-cell and a myeloma cell line), the recombinant antibody is immortalised from the genetic sequence encoding the part of the immunoglobulin that determines binding to the target protein (the antigen binding site). These sequence sets can be cloned into an imunoglobulin G (IgG) expression vector, and after transfection into a cell line (for example HEK293, or Chinese Hamster Ovary-derived CHO), the production of the IgG with that specific antigen binding site by this cell line is achieved. The known DNA sequences guarantee that the clone can never be lost as these sequences can be resynthesised indefinely and recloned back into the IgG expression vector whenever necessary. The potential risk of loss of the original clone by genetic drift, hybridoma instability, etc., associated with monoclonal antibodies, is avoided.
DNA sequences of the antigen binding site
The antigen binding site is defined by the variable regions (also known as the Complimentarity Determining Regions or CDRs) of the antibody. They are built from parts of the heavy chain (VH) and the light chain (VL), located at the tip of each arm of the immunoglobulin. The smallest part of the antibody with the complete antigen binding site would be the Variable Fragment (Fv), existing of only the VH and VL regions. Such Fv has to be stabilised either by linking the two regions by a soluble and flexible peptide (creating a single chain Fv, scFv), or by involving the constant domains CL1 and CH1 to create an antigen binding fragment (Fab). The DNA sequence of the scFv or Fab is used as the defining identity of a recombinant antibody (5).
Recombinant antibody formats
Either the scFv or the Fab can be attached to the constant fragment (Fc) of choice through genetic reconstruction to recreate the complete Immunoglobulin. Smaller formats are in use as well: for example the minibody comprising the scFv attached to the CH3 domains, or the scFab that allows greater stability compared to the Fab (see Figure).
Why Recombinant antibodies
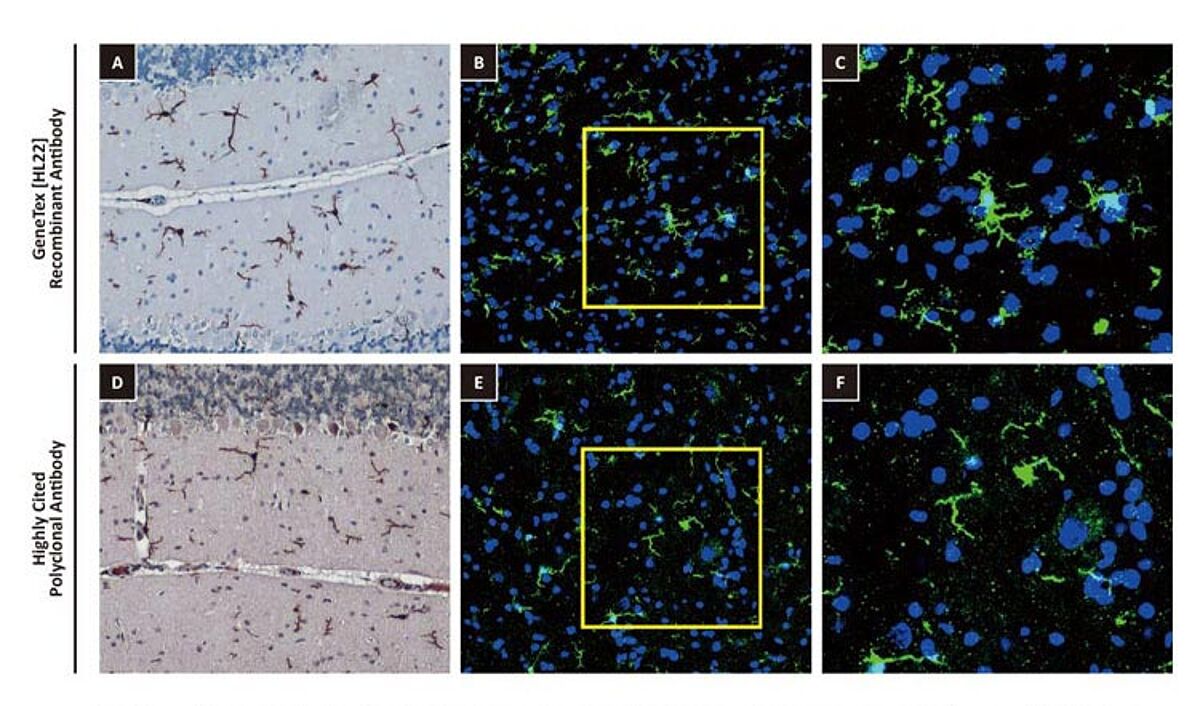
One outstanding advantage of this protocol is that the suitability of the individual clones for desired applications can be tested during screening. For example, GeneTex’s Iba1 rabbit recombinant antibody [HL22] (GTX635363) detects Iba1, a protein commonly used as an immunohistochemical marker of both quiescent and activated microglia. In its development and production, both paraffin- and frozen-IHC analyses (IHC-P, IHC-Fr, respectively) were conducted in the first screening process to identify the best clones for these applications, as shown below (Figure 1). The clones were compared to a highly cited, market-leading commercial antibody to gauge their performance. This strategy provides us with valuable perspective on a clone’s market competitiveness during development. In addition, our recombinant antibody team has successfully expressed the antigen-binding regions of this antibody in the context of both mouse and rat IgG backbones, thus extending flexibility for multiple staining.
More about GeneTex recombinant antibodies
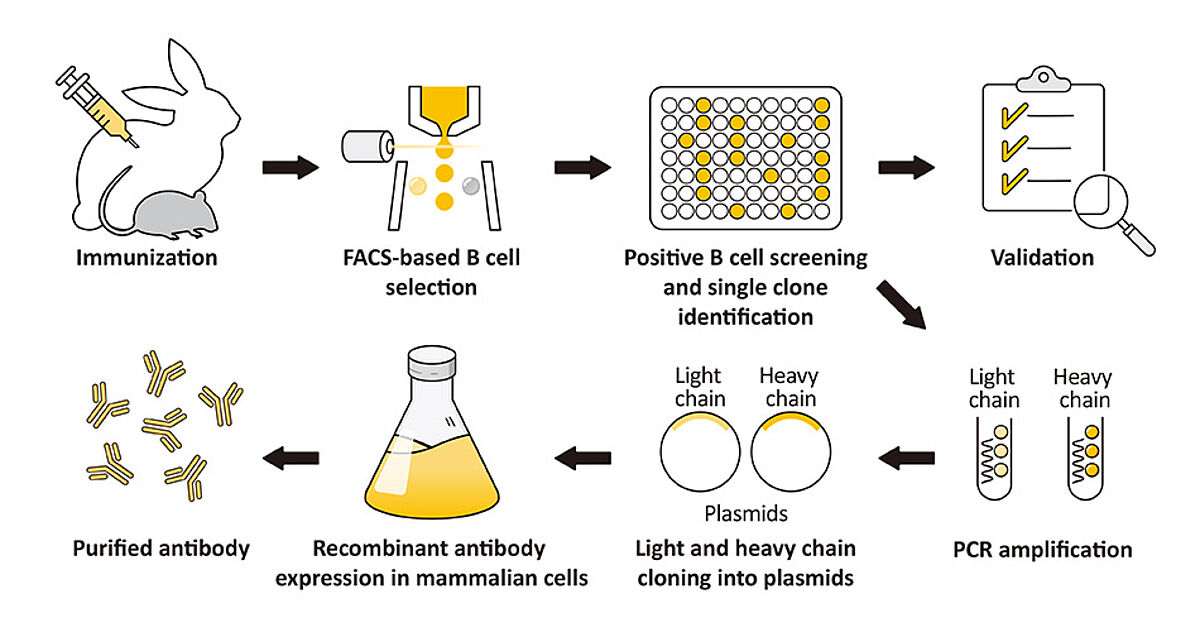
GeneTex’s recombinant antibody protocol employs a multi-parameter FACS-based approach to isolate antigen-specific IgG+ memory B cells from an immunized animal, with subsequent cloning of the antibody variable-region genes into an IgG backbone and expression in mammalian cells. This protocol is very rapid and can be completed in weeks, and also affords the opportunity to identify antibodies with diverse capabilities in various applications.
GeneTex’s rAb protocol employs a multi-parameter FACS-based approach to isolate antigen-specific IgG+ memory B cells from an immunized animal, with subsequent cloning of the antibody variable-region genes into an IgG backbone and expression in mammalian cells. This protocol is very rapid and can be completed in weeks, and also affords the opportunity to identify antibodies with diverse capabilities in various applications. Importantly, it allows cloning of the heavy and light chains from the same B cell, thereby preserving natural pairing. And once cloned, the supply of a given rAb is inexhaustible with exceptional reproducibility.
World's second largest recombinant antibody manufacturer
- 24 h ex stock Zurich for topselling products
Discover more GeneTex products
Download the latest version of GeneTex's Recombinant Antibodies brochure.
Selected Suppliers for recombinant antibodies:

GeneTex’s rAb protocol employs a multi-parameter FACS-based approach to isolate antigen-specific IgG+ memory B cells from an immunized animal. Once cloned, the supply of a given rAb is inexhaustible with exceptional reproducibility.

Absolute Antibody offers a wide range of human-derived antibodies specific to viral pathogens or self-antigen. The proprietary cloning platform allows to produce high-quality recombinant versions of these antibodies.
See Absolute Antibody's recombinant antibodies

Bethyl has applied B-cell sorting and recombinant DNA technology to deliver high quality recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies (RmAbs). Their stringent validation strategy ensures that the antibody is on target and will work in the applications stated.

